文章参考:http://kmanong.top/kmn/qxw/form/article?id=18053&cate=45
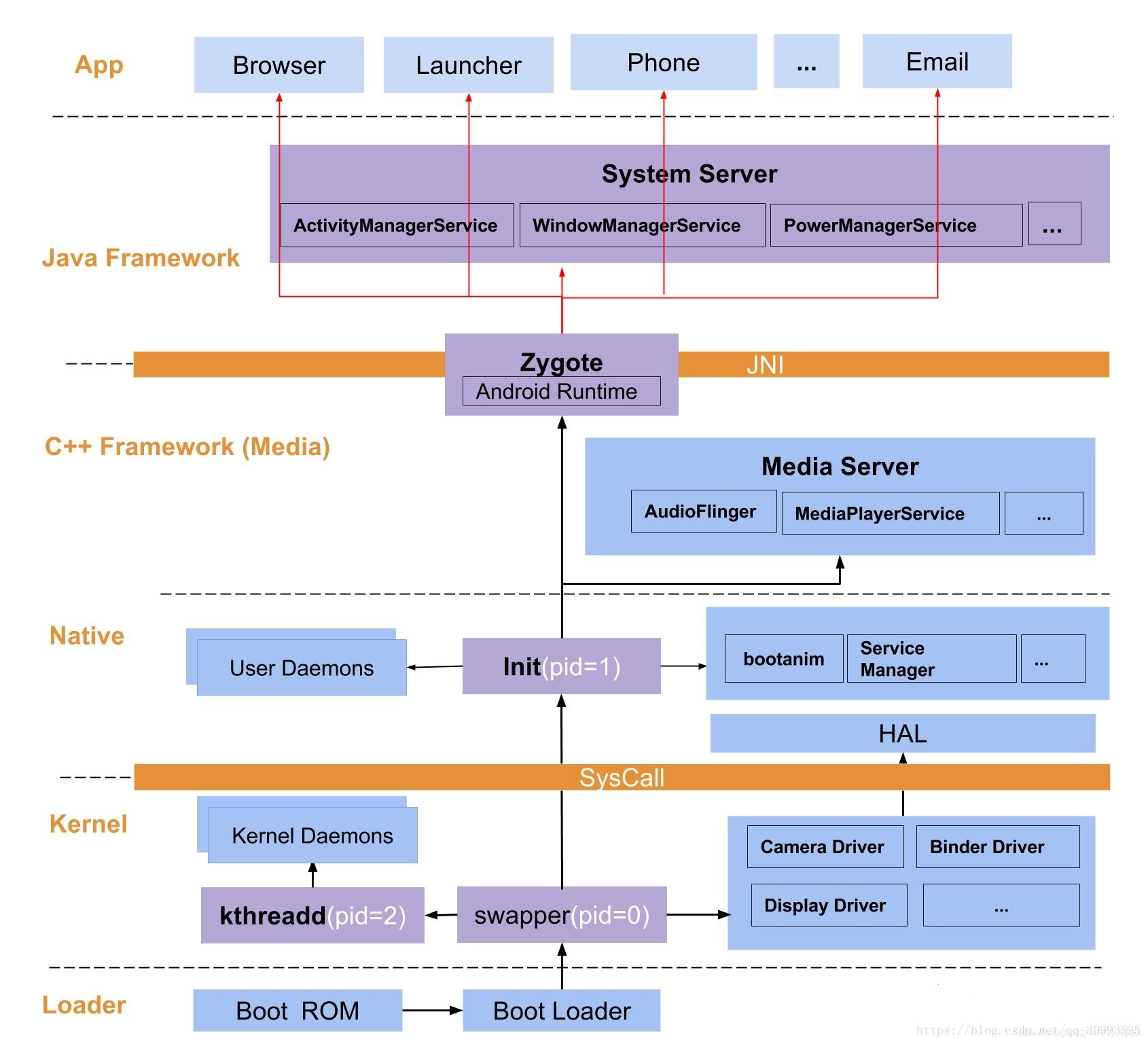
我们都知道Android中非特殊进程(除init进程和Zygote进程外的进程,源码中称其为unspecialized app process),都是由Zygotefork出来的子进程,包括SystemServer,也是由Zygote fork出来的。
那么Zygote进程到底是个什么东西?
在Android系统中,DVM(Dalvik虚拟机)、应用程序进程以及运行系统的关键服务的SystemServer进程都是由Zygote进程来创建的,我们也将它称为孵化器。它通过fock(复制进程)的形式来创建应用程序进程和SystemServer进程,由于Zygote进程在启动时会创建DVM,因此通过fock而创建的应用程序进程和SystemServer进程可以在内部获取一个DVM的实例拷贝。
这篇文章我们主要来探讨以下几个问题:
-
Zygote进程是如何启动的?
-
Zygote又是如何fork出SystemServer的?
-
其他普通进程又是通过什么方式被fork出来的?
-
跟普通的App process有什么区别?
源码分析
init启动zygote时主要是调用app_main.cpp的main函数中的AppRuntime的start来启动zygote进程的,我们就从app_main.cpp的main函数开始分析,如下所示。
App#main函数
/**
* 代码位于:frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
**/
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 argv_String;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) {
argv_String.append("\"");
argv_String.append(argv[i]);
argv_String.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("app_process main with argv: %s", argv_String.string());
}
// 创建AppRuntime,AppRuntime是AndroidRuntime的子类对象
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
// ......
const char* spaced_commands[] = { "-cp", "-classpath" };
// Allow "spaced commands" to be succeeded by exactly 1 argument (regardless of -s).
bool known_command = false;
// ......
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
// 根据zygote.rc解析传进来的参数,进行对比。具体的参数解析:system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64.rc
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
// 需要执行zygote的指令
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
//给 niceName 赋值为zygote
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
// 为启动startSystemServer的标志为赋值。如果是init.zygote64.rc里面肯定会启动SystemServer
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
// 根据参数判断是否为application.具体使用如下:
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/WrapperInit.java
// 标记其为独立的Application进程。不是zygote进程
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
Vector<String8> args;
// 如果是zygote,则className为空,所以此处实际上是判断是否为zygote的进程
if (!className.isEmpty()) {
// 判断非zygote模式时,只需要传递application的参数
// We're not in zygote mode, the only argument we need to pass
// to RuntimeInit is the application argument.
//
// The Remainder of args get passed to startup class main(). Make
// copies of them before we overwrite them with the process name.
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i);
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 restOfArgs;
char* const* argv_new = argv + i;
int argc_new = argc - i;
for (int k = 0; k < argc_new; ++k) {
restOfArgs.append("\"");
restOfArgs.append(argv_new[k]);
restOfArgs.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("Class name = %s, args = %s", className.string(), restOfArgs.string());
}
} else {
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
// classname为空,当前为zygote模式。如果startSystemServer为true.则增加启动SystemServer的参数
if (startSystemServer) {
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
// 获取支持的CPU指令集
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
}
// 此处为zygote模式,需要把所有参数都传递过去
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
}
// niceName不为空,说明是zygote模式
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
}
// 如果是zygote模式
if (zygote) {
// 调用zygoteInit函数,并把当前的参数传递过去
// 这里调用runtime的start函数来启动zygote进程,
// 并将args传入,这样启动zygote进程后,zygote进程会将SystemServer进程启动。
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (!className.isEmpty()) {
// 如果是非zygote模式
//调用RuntimeInit函数
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
}
如果startSystemServer为true的话(默认为true),将”start-system-server”放入启动的参数args。
调用runtime的start函数来启动zygote进程,并将args传入,这样启动zygote进程后,zygote进程会将SystemServer进程启动。
这篇文章的目的是分析zygote的流程。所以我们只需看看runtime.start(“com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit”, args, zygote) 调用zygoteInit函数,并把当前的参数传递过去
我们知道runtime指的就是AppRuntime,AppRuntime声明也在app_main.cpp中,它继承AndroidRuntime,也就是我们调用start其实是调用AndroidRuntime的start函数:
AndroidRuntime#start函数
/*
* 代码位于:frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
* and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
* named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid());
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
// Whether this is the primary zygote, meaning the zygote which will fork system server.
// 判断这个是否是主zygote,即是否需要进行fork system server
bool primary_zygote = false;
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
primary_zygote = true;
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
}
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /system does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
const char* artRootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ART_ROOT");
if (artRootDir == NULL) {
LOG_FATAL("No ART directory specified with ANDROID_ART_ROOT environment variable.");
return;
}
const char* i18nRootDir = getenv("ANDROID_I18N_ROOT");
if (i18nRootDir == NULL) {
LOG_FATAL("No runtime directory specified with ANDROID_I18N_ROOT environment variable.");
return;
}
const char* tzdataRootDir = getenv("ANDROID_TZDATA_ROOT");
if (tzdataRootDir == NULL) {
LOG_FATAL("No tz data directory specified with ANDROID_TZDATA_ROOT environment variable.");
return;
}
//const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
//ALOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
/* start the virtual machine */
// 调用startVm函数来创建JavaVm(DVM)
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
// TODO jni环境的初始化??
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote, primary_zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
* 调用startReg函数用来为DVM注册JNI
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
//根据启动参数创建数组
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
//从app_main的main函数得知className为com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
//找到ZygoteInit的main函数
//其中startClass从app_main的main函数得知为com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
//通过JNI调用ZygoteInit的main函数
// 注释4处通过JNI调用ZygoteInit的main函数,因为ZygoteInit的main函数是Java编写的,因此需要通过JNI调用。
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
经过这轮的调用,我们代码终于走到jni的逻辑里面。通过这里jni的调用我么开始调用到ZygoteInit的main函数。也就是startClass从app_main的main函数得知为com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit中的main函数。
ZygoteInit#main函数
/**
* 代码位于:/framework/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
* This is the entry point for a Zygote process. It creates the Zygote server, loads resources,
* and handles other tasks related to preparing the process for forking into applications.
*
* This process is started with a nice value of -20 (highest priority). All paths that flow
* into new processes are required to either set the priority to the default value or terminate
* before executing any non-system code. The native side of this occurs in SpecializeCommon,
* while the Java Language priority is changed in ZygoteInit.handleSystemServerProcess,
* ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc, and Zygote.usapMain.
*
* @param argv Command line arguments used to specify the Zygote's configuration.
*/
public static void main(String argv[]) {
//用来管理和子进程通信的socket服务端
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
//这里其实只是设置一个标志位,为创建Java线程时做判断处理,如果是zygote进程,则不需要开启线程
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
//为zygote进程设置pgid(Process Group ID),
// 详见:`https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41498383/what-do-the-identifiers-pid-ppid-sid-pgid-uid-euid-mean`
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
Runnable caller;
try {
// Store now for StatsLogging later.
final long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
//获取系统属性,判断系统重启完成
final boolean isRuntimeRestarted = "1".equals(
SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"));
//判断当前进程是64位程序还是32位程序,并设置标记
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.preForkInit();
// 解析参数前的默认参数值
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String zygoteSocketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
//对参数进行解析
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
//参数重包含`start-system-server`
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
//设置标志为位true
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
//获取支持的架构列表
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
zygoteSocketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
final boolean isPrimaryZygote = zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
if (!isRuntimeRestarted) {
if (isPrimaryZygote) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
startTime);
} else if (zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME)) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
startTime);
}
}
//如果支持架构为空,直接抛出异常
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
}
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
//调用ZygoteHooks.gcAndFinalize()进行垃圾回收
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
//jni调用初始化zygote的状态,是否为isPrimaryZygote
Zygote.initNativeState(isPrimaryZygote);
//结束zygote创建,其实内部是调用`runtime`给`zygote_no_threads_`赋值为false,为创建本地线程做准备
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
//创建zygoteServer,为其他进程初始化创建时与zygote通信做准备
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
//判断是否需要startSystemServer
if (startSystemServer) {
//通过fork的方式开启zygote的子进程,systemServer,并返回一个Runnale对象
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
//如果是zygote进程,则r==null,如果不是zygote进程,也就是systemServer进程,则执行下面的代码
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
// zygote进程进入死循环中,来获取子进程发送的消息
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//如果发生异常,则说明zygote初始化失败,zygoteServer也需要关闭
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
//如果发生异常,则说明zygote初始化失败,zygoteServer也需要关闭
if (zygoteServer != null) {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
zygote的大概流程我们已经梳理完了,现在我们来总结一下
-
解析对应的
zyogte.rc脚本 -
调用
app_process/appMain.cpp -
设置进程名为zygote
-
调用
zygoteInit.java初始化zygote进程 -
JNI调用
zygoteInit.cpp完成进程创建 -
调用
runSelectionLoop(),接收其他进程发送的消息创建子进程
SystemServer启动
我们都知道,Android系统中,zyogte进程是Java世界的首个进程(init进程为头号进程),是直接通过exec的系统调用创建的,其他的进程,包括system_server,都是zygote进程的子进程,那我们接下来从源码的角度来看一下,zygote是如何fork出system_server的
由上面的分析我们看到,根据zygote.rc的参数,解析出是否需要startSystemServer,如果为true,则调用forkSystemServer来fork出子进程SystemServer,并且执行其返回的Runnable的run()方法,我们先来看看forkSystemServer具体做了什么
ZygoteInit#forkSystemServer
/**
* 代码位于:/framework/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
* Prepare the arguments and forks for the system server process.
* 为forkSystemServer进程准备参数,并且创建system server进程
* @return A {@code Runnable} that provides an entrypoint into system_server code in the child
* process; {@code null} in the parent.
*/
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
//Linux使用POSIX capabilities代替传统的信任状模型
//设置进程权能
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK, //允许锁定共享内存片段
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,//允许对不属于自己的进程发送信号
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,// 允许执行网络管理任务:接口、防火墙和路由等
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,//允许绑定到小于1024的端口
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,//允许网络广播和多播访问
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,//允许网络广播和多播访问
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,//插入和删除内核模块
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,//允许提升优先级,设置其它进程的优先级
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,//允许配置进程记帐
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME, //允许改变系统时钟
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,//允许配置TTY设备
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM,
OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND
);
/* Containers run without some capabilities, so drop any caps that are not available. */
StructCapUserHeader header = new StructCapUserHeader(
OsConstants._LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, 0);
//用户权能数据
StructCapUserData[] data;
try {
//获取进程权能,存储到data中
data = Os.capget(header);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to capget()", ex);
}
capabilities &= ((long) data[0].effective) | (((long) data[1].effective) << 32);
/*使用硬编码的方式定义出启动system server的参数字符串args*/
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,"
+ "1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010,3011",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,//进程权能
"--nice-name=system_server",//进程niceName
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteArguments parsedArgs = null;
//processId,进程id
int pid;
try {
//创建ZygoteArguments对象,把args解析为需要的参数
parsedArgs = new ZygoteArguments(args);
Zygote.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
Zygote.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
if (Zygote.nativeSupportsTaggedPointers()) {
/* Enable pointer tagging in the system server. Hardware support for this is present
* in all ARMv8 CPUs. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_TBI;
}
/* Enable gwp-asan on the system server with a small probability. This is the same
* policy as applied to native processes and system apps. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.GWP_ASAN_LEVEL_LOTTERY;
if (shouldProfileSystemServer()) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
}
//fork创建SystemServer
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
//pid为0,则说明是zygote进程,进行最后的收尾工作
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
我们看一下,这个方法还是只是进行参数的参数解析。代码最后调用了Zygote.forkSystemServer()来创建SystemServer,我们接着来跟一下:
Zygote#forkSystemServer
static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) { //内部调用ART的Runtime对zygote的线程池的线程进行清理 ZygoteHooks.preFork(); //JNI调用,真正创建systemServer进程的函数 int pid = nativeForkSystemServer( uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities); // Set the Java Language thread priority to the default value for new apps. Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon(); return pid; }
接着跟下去,到c++的本地代码中 zygote.cpp
/**
* 代码位于:frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
**/
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer(
JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids,
jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permitted_capabilities,
jlong effective_capabilities) {
std::vector<int> fds_to_close(MakeUsapPipeReadFDVector()),
fds_to_ignore(fds_to_close);
fds_to_close.push_back(gUsapPoolSocketFD);
if (gUsapPoolEventFD != -1) {
fds_to_close.push_back(gUsapPoolEventFD);
fds_to_ignore.push_back(gUsapPoolEventFD);
}
if (gSystemServerSocketFd != -1) {
fds_to_close.push_back(gSystemServerSocketFd);
fds_to_ignore.push_back(gSystemServerSocketFd);
}
//从zygote进程fork出子进程,并返回processId
pid_t pid = ForkCommon(env, true,
fds_to_close,
fds_to_ignore,
true);
if (pid == 0) {
// System server prcoess does not need data isolation so no need to
// know pkg_data_info_list.
SpecializeCommon(env, uid, gid, gids, runtime_flags, rlimits,
permitted_capabilities, effective_capabilities,
MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT, nullptr, nullptr, true,
false, nullptr, nullptr, /* is_top_app= */ false,
/* pkg_data_info_list */ nullptr,
/* whitelisted_data_info_list */ nullptr, false, false);
} else if (pid > 0) {
// The zygote process checks whether the child process has died or not.
ALOGI("System server process %d has been created", pid);
gSystemServerPid = pid;
// There is a slight window that the system server process has crashed
// but it went unnoticed because we haven't published its pid yet. So
// we recheck here just to make sure that all is well.
int status;
if (waitpid(pid, &status, WNOHANG) == pid) {
ALOGE("System server process %d has died. Restarting Zygote!", pid);
RuntimeAbort(env, __LINE__, "System server process has died. Restarting Zygote!");
}
if (UsePerAppMemcg()) {
// Assign system_server to the correct memory cgroup.
// Not all devices mount memcg so check if it is mounted first
// to avoid unnecessarily printing errors and denials in the logs.
if (!SetTaskProfiles(pid, std::vector<std::string>{"SystemMemoryProcess"})) {
ALOGE("couldn't add process %d into system memcg group", pid);
}
}
}
return pid;
}
到这里我们就把相关源码分析完了,我们来总结下:
-
解析
zygote.rc的相关脚本,获取startSystemserver的属性字段 -
调用
startSystemServer() -
调用
forkSystemServer(),为当前进程赋予权限,并设置UID,GID -
创建ZygoteArgument,调用
zygote.forkSystemServer -
JNI调用native的函数,
nativeForkSystemServer完成进程的fork工作

 概述
概述
评论(0)